On May 22nd, the European Commission released the first batch of national risk classification lists for the EU Zero Deforestation Act (EUDR).
The list categorizes countries/regions into three levels of high risk, standard risk, or low risk based on the degree of deforestation and forest degradation during the production of relevant EUDR commodities.
Among them, China is listed as a low-risk country, and due diligence requirements will be simplified.
The above risk levels will directly affect the due diligence obligations of companies as operators when launching or exporting products made of soybeans, beef, palm oil, wood, cocoa, coffee, and rubber in the EU market.
This benchmark system will play a key role in the effective implementation of EUDR, with large enterprises taking effect on December 30, 2025, and some micro and small enterprises taking effect on June 30, 2026.
Evaluation Criteria
According to Article 29 of the EUDR Act, the committee evaluates countries based on quantitative and qualitative indicators.
The key quantitative criteria include the historical rate of deforestation and forest degradation, the expansion of agricultural land related to related commodities, and the production and trade trends of the seven EUDR commodities and their derivatives.
Qualitative factors include information submitted by countries themselves and other stakeholders, including agricultural and forestry carbon emissions and removals related to the Paris Agreement, cooperation agreements between countries and the European Union or its member states, the strength of national legal frameworks and enforcement capabilities, human rights and indigenous protection, data transparency, and the status of international sanctions.
National benchmark risk results
The first batch of national benchmark lists shows that the vast majority of countries/regions are classified as low-risk countries/regions.
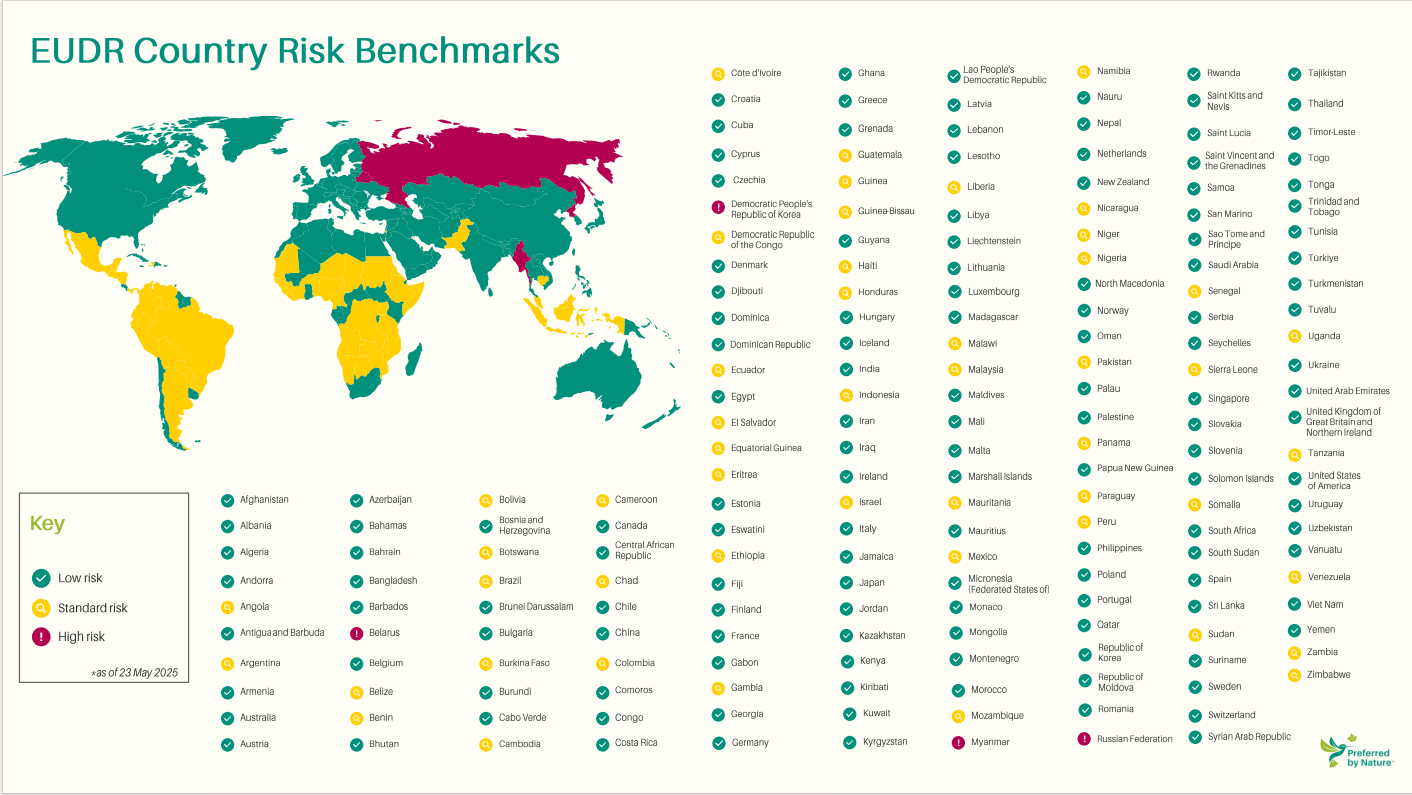
There are four high-risk countries/regions, namely Belarus, Myanmar, North Korea, and Russia. Imported products from these countries (if not already banned) will undergo the strictest compliance checks.
There are 50 standard risk countries/regions, mainly countries/regions with high forest coverage such as Brazil and Indonesia. Despite its high historical deforestation rate, it is still classified as a standard risk country/region. This means that under the bill, they will face moderate scrutiny.
Low risk countries/regions include countries such as the United States, Canada, and China, all EU member states, and 140 countries/regions such as Ukraine and Thailand.
According to the requirements, the national authorities of EU member states must adjust their enforcement efforts based on the risk level of the country/region. The annual inspection must cover the following content.
Low risk countries/regions: At least 1% of relevant operators place, provide, or export related products in the market.
Standard risk countries/regions: at least 3% of relevant operators.
High risk countries/regions: at least 9% of relevant operators and 9% of relevant product quantities.